
Suspended chords AKA ‘sus chords’ are simply Each may also transition more smoothly between other chords in your progressions, without changing the pitch of your G chord: G Major Suspended chords. G Major (1st Inversion): G Major (2nd Inversion): Try playng the inversions together with the root – the voicings create quite different textures. Perhaps this is easier to understand in a simple chart: Chord The ‘voice leading’ each respective chord is G, B, and D. In the image above, we can see the default triad, 1st inversion and 2nd inversion. This has the effect of changing which note is at the root of the chord. It can seem a bit confusing, at first, but it’s super useful when you get your head around it!Īs discussed earlier, ‘inversions’ are ways of playing the same chord but with one or more of the same notes played in a different octave. You can choose which ‘version’ of the chord to play. The lower D is one whole octave below the higher one.ĭo you see that this is an example of the same chord with the one played on a different octave? This is a ‘version’ of the root chord – or, as we call it in music theory, an ‘Inversion’. D is 7 semitones up from G, and therefore 5 semitones down from it, too. Remember that an octave is made up of 12 semitones? In the chord of G, the fifth is D. Regardless of scale, the 1st and 5th together always signify which chord is being played. The 1st and 5th notes are the over-arching chord tones.

The middle note, or third, is what signifies whether a chord is Major or Minor. So, we can count five keys (or 3 whole notes) up from G to reach the third – B. On a piano, a semi-tone step is simply a key up or down from the current key.
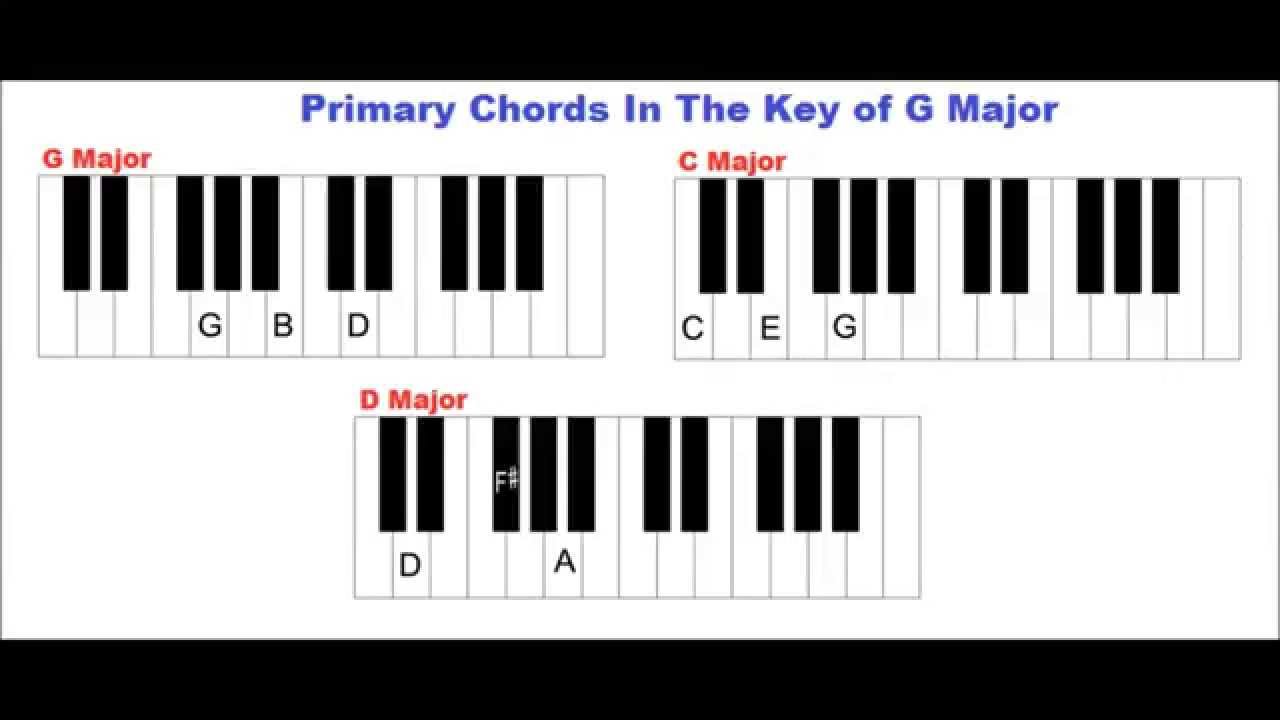
We call this note the ‘third’ because it is three whole notes from the root, G. In G Major, the middle note is 5 semitones above the root. The number of semitones between each note varies if the chord is Major or Minor. Starting from the root, triad chords contain 2 additional chord tones. We already have the Root, third and fifth present in the basic triad. These additional notes are called ‘chord tones’. You can add notes, or ‘complexity’ to this G Major triad and increase the polyphony. The basic triad of G Major looks like this: Chord Learn how to use the chord and key of G Major with our guide! It’s one of the most common chords in modern music and the root key of many smash-hit songs. The chord and key of G Major (and how to use it in your songs).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
